Edge Computing
The term “edge” is a reference to geographic distribution. Instead of relying on the cloud for all work Edge computing is done in situ, close to or at the data source.
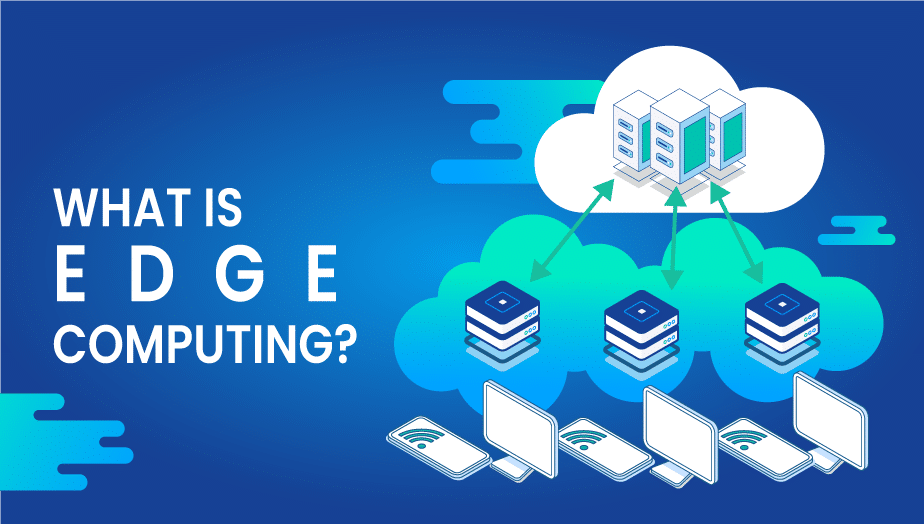
Edge computing or computing on the edge of the data stream is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation as well as data storage closer to data sources. The speed of response and bandwidth are expected to rise as a consequence. It’s not a tech It’s architecture.
As opposed to other forms of computer networks, this form is topology and location-sensitive. The data is exchanged and received at the edge of the system, which is where edge computing happens. The design reduces latency and delay, which allows for quicker processing.
By enabling faster responses to user actions and data that is at the edge, programs and applications can boost overall performance and the user experience.
Edge Computing uses the untapped computational power on Edge nodes, which include routers, stations, and switches to shift some of the computation to the edges instead of relying on central servers to do this.
Why edge computing?
Enterprise-grade applications run faster and more efficiently on edge computing than traditional methods.
There were times when edge points generated large amounts of unused data. The Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile computing have allowed IT architecture to be decentralized, allowing organizations to gain near real-time insights with less latency, lower cloud server bandwidth demands, and better security.
Using edge computing by businesses enables workers to access the data they need more quickly to perform their job duties. Also, workers have access to the necessary equipment without interruptions or errors that can easily be prevented in innovative workplaces with automation and predictive maintenance.
In edge computing, large amounts of data are analyzed rapidly at or near the location where the data is collected so that enterprises can optimize daily operations.
It is easier to process gathered data than to send it to a centralized cloud or a primary data center several time zones away, which would cause too much network lag and performance problems.
There are various computing tasks, and an architecture suitable for one kind of computing task might not be ideal for another.
Using edge computing to deploy compute and storage resources closer to the point of the data source has developed into a viable and essential architecture that supports distributed computing.
Generally, distributed computing models are not new, and concepts like remote offices, branch offices, data center colocation, and cloud computing are well established. This short explanation of edge computing gives you a good idea of its importance.
Which are the primary use cases for edge computing?
A hybrid computing model can be augmented with edge computing to accomplish the following:
- Monitoring of hospitalized patients.
- Smart cities
- Cloud gaming
- Virtualized radio networks and 5G
- Coordinating operations across geographies
- Autonomous vehicles
- Augmented reality/virtual reality
Edge computing offers the benefit of optimizing resources. A minimal amount of bandwidth is used by deploying only those services and functionality required to resolve an issue. In case of a data center or cloud failure, the service will still operate and maintain remote resilience.
It is now time to examine some advantages and disadvantages of Edge computing.
Benefits of edge computing
With the rise of 5G networks worldwide, edge computing is, in many ways, the next evolution of cloud computing. The IT infrastructure needed in previous generations is no longer necessary for companies to harness comprehensive data analysis.
Furthermore, edge computing can be used in numerous ways, including monitoring security and health, conducting self-driving vehicle trials, and enhancing customer service.
Reliable and resilient: With edge computing, data can still be fetched and processed with little or no hindrances, even with poor internet connectivity.
Savings on IT costs: By handling data locally rather than in the cloud, edge computing helps businesses save on IT expenses. Edge computing lowers companies’ cloud processing and storage costs by eliminating unnecessary data at or near the collection point.
Autonomy: Edge computing is practical where connectivity is unreliable, or bandwidth is restricted because of the site’s environmental characteristics.
Reduced operational costs: Businesses spend a lot of money moving data around on cloud hosting services. These centralized hosting providers charge more for moving more data, so the more data they move, the more money they spend.
Edge Security: Edge computing presents a unique security implementation and assurance opportunity. Data security and safety remain concerns for enterprises, even as cloud providers provide IoT services and specialize in complex analysis.
Faster response times: Companies can process data faster and reliably by bypassing centralized cloud and data center locations. When sending information from thousands of sensors, cameras, or other intelligent devices simultaneously to a central office, latency, network bottlenecks, and diminished data quality are likely to occur.
Deficiencies of edge computing
Even though edge computing offers many benefits, such as processing data close to the source, it also creates several challenges for the network.
Less robust infrastructure: Data Centers without complete infrastructure usually need to overcome some technical challenges because they lack the whole infrastructure of Core Data Centers.
The limit of capability: Besides the variety and scale of resources and services offered by cloud computing, edge computing has its limitations. While deploying infrastructure at the edge can be effective, it must be clearly defined what it will do and how it will work. An extensive edge computing deployment will serve a specific purpose at a predetermined scale using limited resources.
Complexity: Building a distributed system is much more complex than building a centralized Cloud architecture. Various interfaces are available to communicate between different components of an edge computing environment that uses new technologies, and other manufacturers produce them.
The purpose of this article is to introduce what is edge computing, why it is important, and some of the advantages and disadvantages of edge computing.
Hopefully you now understand what edge computing is and whether it is right for your organization. Let us know what you think about this.
FAQ
Edge computing is a distributed computing model where data processing and storage are done closer to the data source, such as sensors or IoT devices, rather than in a centralized data center. This reduces latency, improves response time, and conserves bandwidth.
Edge computing is different from cloud computing in that it processes and stores data closer to the source, while cloud computing processes and stores data in centralized data centers. Edge computing is designed for real-time, low-latency applications, while cloud computing is designed for applications that can handle some delay in processing.
Edge computing can be used in various applications, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT, smart cities, and healthcare. For example, edge computing can enable real-time data processing from sensors and cameras in autonomous vehicles to improve safety and reliability.
Edge computing offers several benefits, such as reduced latency, improved response time, better reliability, increased security, and reduced bandwidth consumption. It also enables real-time processing of data, which is critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles and industrial IoT.
One of the main challenges of implementing edge computing is the need for specialized hardware and software, which can be expensive and challenging to deploy and maintain. There is also a need for skilled personnel to manage and operate edge computing infrastructure.
Businesses can start with edge computing by identifying the use cases best suited for edge computing, selecting the proper hardware and software, and building the necessary infrastructure. They can also partner with third-party providers that offer edge computing services to simplify deployment and management.