How to Install GUI on Debian
Graphical User Interface (GUI) on Debian
Debian is a popular Linux-based operating system known for its stability, security, and flexibility. It is widely used in servers, workstations, and embedded systems. Debian is also available with several desktop environments that provide a GUI for end-users to interact with the system. This article will explore the GUI on Debian, including its features, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases.
What is GUI on Debian?
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) on Debian is a visual interface that allows users to interact with the system using graphics and icons rather than typing commands into the terminal. The GUI on Debian includes a desktop environment, window manager, display server, and various applications that allow users to perform multiple tasks, such as browsing the web, editing documents, managing files, and more.
Compared to other systems, GUI on Debian offers several advantages of GUI on Debian:
- Debian is a highly customizable system. Users can choose from desktop environments, such as GNOME, KDE, Xfce, and LXDE, each with features and visual style.
- The GUI on Debian is highly stable and reliable, making it ideal for mission-critical applications that require high uptime and availability.
- The GUI on Debian is highly secure and provides several security features, such as firewall and encryption, to protect the system and user data.
We’ll now install the desktop for your Debian system.
For Debian systems to be registered with VPSie, you need to create a VPSie account if you don’t have one already.
First we are going to update our system by running the following command:
# apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y
Next, install the desktop environment:
# sudo apt -y install task-gnome-desktop
If you have successfully installed the desktop environment, run the following command to set a graphical login.
# sudo systemctl set-default graphical.target
We will now commend a line in the file gdm-password. Run the following command to open it and comment(add # infront of the line) the line.
# sudo nano /etc/pam.d/gdm-password
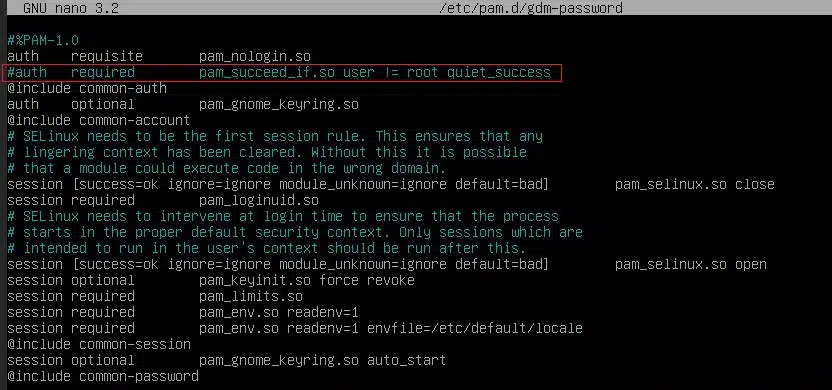
We are ready to use the GUI now. Do a system reboot to finish the process:
# sudo reboot
Your Debian instance is configured with GNOME desktop, which has successfully installed, Explore it. It is our hope that you have enjoyed this article.
Use cases for GUI on Debian.
The GUI on Debian is suitable for various use cases, from personal computing to enterprise-level applications. Some everyday use cases for GUI on Debian include:
- Desktop computing: The GUI on Debian is suitable for desktop computing, allowing users to browse the web, edit documents, manage files, and more.
- Server administration: The GUI on Debian can be used for server administration tasks, such as monitoring system performance, managing user accounts, and configuring network settings.
- Development: The GUI on Debian is popular among developers, as it provides various tools and applications for software development, such as IDEs, code editors, and debugging tools.
- Education: The GUI on Debian is used in educational institutions for teaching and learning purposes, as it provides a user-friendly interface for students and teachers.
Features of GUI on Debian
The GUI on Debian includes several features and components that make it a powerful and versatile system. Some of the critical elements of the GUI on Debian include:
- Desktop environment: Debian includes several desktop environments, such as GNOME, KDE, Xfce, and LXDE, each with features and visual style.
- Window manager: The window manager is accountable for managing the windows on the desktop, including their placement, size, and appearance.
- Display server: The display server is responsible for rendering and displaying graphics on the screen. Debian uses the X Window System (X11) as the default display server.
- Taskbar: The taskbar is a panel that displays running applications, system status, and other information.
- Launcher: The launcher is an application that provides access to other applications and system features.
- System settings: The system settings provide a centralized location for configuring system settings, such as network, sound, display, and more.
- Control panel: The control panel provides various administrative tools for managing the system, such as user accounts, network settings, etc.
- Theme customization: Debian allows users to customize the desktop’s appearance, including the theme, icons, and wallpaper.
- App launcher: The app launcher provides a quick and easy way to launch applications.
- File manager: The file manager allows users to browse and manage files and directories on the system.
Advantages of GUI on Debian
The GUI on Debian offers several advantages over other systems, including:
- Stability: Debian is known for its steadiness, and the GUI on Debian is no exception. It provides a reliable and stable platform for end-users, making it suitable for mission-critical applications that require high uptime and availability.
- Security: Debian is also known for its security, and the GUI on Debian provides several security features, such as firewall and encryption, to protect the system and user data.
- Customizability: Debian is highly customizable, and users can choose from several desktop environments, each with its own set of features and visual style. This makes the GUI on Debian highly versatile and suitable for various use cases.
- Flexibility: Debian is a highly flexible system, and the GUI on Debian is no exception. It provides various tools and applications for different tasks, making it suitable for personal computing, enterprise-level applications, and more.
Disadvantages of GUI on Debian
Despite its many advantages, the GUI on Debian also has some disadvantages. Some of the critical weaknesses of the GUI on Debian include the following:
- Learning curve: The GUI on Debian can be difficult to learn for users who need to become more familiar with Linux-based operating systems. This can make it challenging for new users to get started with Debian.
- Resource-intensive: Some desktop environments, such as GNOME and KDE, can be resource-intensive, requiring a powerful hardware configuration to run smoothly.
- Limited software availability: Debian includes a range of applications, and some users may find that their favorite software is unavailable in the Debian repositories. This can be a drawback for users who rely on specific software for their work.
Conclusion
The GUI on Debian is a powerful and versatile system providing end-users with various features and components. It is highly customizable, stable, and secure, making it suitable for multiple use cases, from personal computing to enterprise-level applications. Although it has some disadvantages, such as a learning curve and limited software availability, the advantages of the GUI on Debian far outweigh its drawbacks. Overall, Debian is a reliable and flexible system that offers a user-friendly interface for end-users.
FAQ
A GUI, or Graphical User Interface, is a visual interface that allows users to interact with their computer using icons, buttons, and windows, rather than typing commands in a terminal. A GUI makes it easier for users to navigate and use their computer, especially for those who are not familiar with the command line.
Debian is a Linux distribution that is known for its stability and efficiency, but it does not come with a GUI installed by default. To install a GUI on Debian, you’ll need to first update and upgrade the system packages, then install a desktop environment or a window manager. Some popular desktop environments include GNOME, KDE, and XFCE, while window managers like Openbox and Fluxbox are lighter and faster alternatives.
To update and upgrade system packages on Debian, you can use the following commands in the terminal:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
The first command updates the package list from the repositories, while the second command installs the latest available versions of the packages on your system.
To install a desktop environment on Debian, you can use the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get install task-desktop
This command will install the default desktop environment, which is GNOME. If you want to install a different desktop environment, you can replace task-desktop with the name of the desktop environment you want to install, such as task-kde-desktop for KDE or task-xfce-desktop for XFCE.
To install a window manager on Debian, you can use the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get install <window-manager>
Replace <window-manager> with the name of the window manager you want to install, such as openbox or fluxbox.
To switch between desktop environments or window managers on Debian, you’ll need to log out of your current session and select the new environment or manager from the login screen. The login screen should show a list of available desktop environments or window managers that you can choose from.
To uninstall a desktop environment or window manager on Debian, you can use the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get remove <desktop-environment-or-window-manager>
Replace <desktop-environment-or-window-manager> with the name of the environment or manager you want to uninstall. This command will remove the packages associated with the environment or manager, but it will not remove any configuration files or user data.
It depends on your needs and preferences. If you’re comfortable using the command line and don’t need graphical applications, then you can use Debian without a GUI. However, if you prefer a visual interface or need to use graphical applications, then installing a GUI can be helpful.