How to uninstall packages on CentOS?
The term package refers to a bundle of things. The Linux operating system may contain unwanted packages that can slow you down. The extra software packages need to be uninstalled from the system because these packages take up a lot of space and slow down the system.
You should remove unused software or related packages from the system if the software or package is not being used. Let’s go through how the method works here.
Find installed packages
You can get a list of all installed software or packages by running the following command in a terminal window.
# yum list | less
OUTPUT
Last metadata expiration check: 1:51:53 ago on Sat 01 Jan 2022 01:52:09 PM EST. Installed Packages abattis-cantarell-fonts.noarch 0.0.25-4.el8 @AppStream acl.x86_64 2.2.53-1.el8 @anaconda adwaita-cursor-theme.noarch 3.28.0-2.el8 @anaconda adwaita-icon-theme.noarch 3.28.0-2.el8 @anaconda at.x86_64 3.1.20-11.el8 @baseos at-spi2-atk.x86_64 2.26.2-1.el8 @anaconda at-spi2-core.x86_64 2.28.0-1.el8 @anaconda atk.x86_64 2.28.1-1.el8 @anaconda audit.x86_64 3.0-0.17.20191104git1c2f876.el8 @anaconda audit-libs.x86_64 3.0-0.17.20191104git1c2f876.el8 @anaconda authselect.x86_64 1.2.2-1.el8 @anaconda authselect-libs.x86_64 1.2.2-1.el8 @anaconda avahi-libs.x86_64 0.7-20.el8 @anaconda basesystem.noarch 11-5.el8 @anaconda bash.x86_64 4.4.19-12.el8 @anaconda bash-completion.noarch 1:2.7-5.el8 @baseos bc.x86_64 1.07.1-5.el8 @baseos bind-export-libs.x86_64 32:9.11.20-6.el8 @anaconda biosdevname.x86_64 0.7.3-2.el8 @anaconda brotli.x86_64 1.0.6-2.el8 @anaconda bzip2-libs.x86_64 1.0.6-26.el8 @anaconda c-ares.x86_64 1.13.0-5.el8 @anaconda ca-certificates.noarch 2020.2.41-80.0.el8_2 @anaconda cairo.x86_64 1.15.12-3.el8 @anaconda cairo-gobject.x86_64 1.15.12-3.el8 @anaconda centos-gpg-keys.noarch 1:8-2.el8 @anaconda centos-stream-release.noarch 8.4-1.el8 @anaconda centos-stream-repos.noarch 8-2.el8 @anaconda chkconfig.x86_64 1.13-2.el8 @anaconda chrony.x86_64 3.5-1.el8 @anaconda
Locate a specific software or package
If you are looking for a specific package or software, use the following command, “Packagename” should be replaced with your desired package.
# yum list packagename
OUTPUT
We used the ‘brotli’ here as an example,
[root@XXX-fb68-CentOS ~]# yum list brotli Last metadata expiration check: 2:04:11 ago on Sat 01 Jan 2022 01:52:09 PM EST. Installed Packages brotli.x86_64 1.0.6-2.el8 @anaconda Available Packages brotli.i686 1.0.6-3.el8 baseos brotli.x86_64 1.0.6-3.el8 baseos
Uninstall software or package
With your package name, run one of the following commands.
# yum remove packagename
Or
# yum erase packagenameOUTPUT
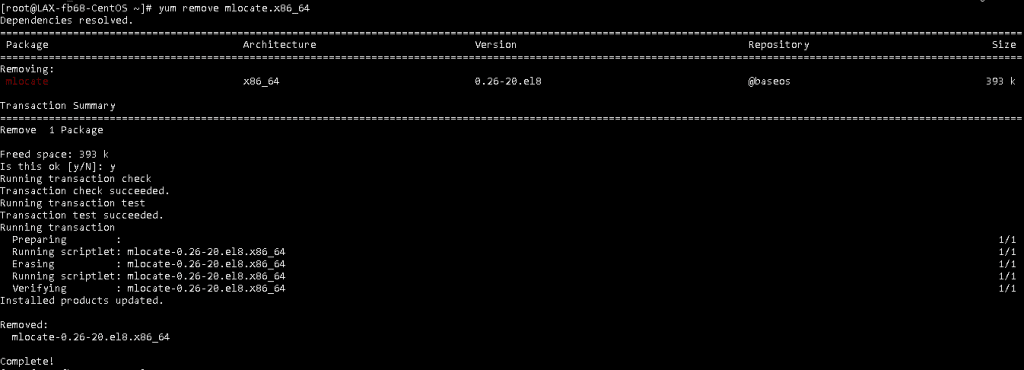
Here is an example of how we uninstalled ‘Mlocate.’
That’s it; thanks for reading! I hope it was informative for you!
FAQ
yum (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) is a command-line package manager in CentOS and other RPM-based Linux distributions. It is used to install, update, and remove packages and their dependencies.
You can uninstall a package using yum on CentOS by running the following command:
sudo yum remove package_name
Replace package_name with the name of the package you want to uninstall. You may need to enter your password to confirm the command.
Yes, you can uninstall multiple packages at once using yum. Simply list the names of the packages you want to uninstall, separated by spaces, after the remove command. For example:
sudo yum remove package1 package2 package3When you uninstall a package using yum, it will remove the package and any dependencies that are no longer needed. If any other packages depend on the package you are trying to remove, they will also be removed.
No, you cannot undo a package removal using yum. Once a package has been removed, it cannot be restored using yum. However, you can reinstall the package if you need it again.
You can reinstall a package using yum by running the following command:
sudo yum reinstall package_name
Replace package_name with the name of the package you want to reinstall.
Yes, you can use the --nodeps option with the remove command to remove a package without removing its dependencies. However, be cautious when using this option, as it can cause issues with other packages that depend on the removed package.
You can see a list of installed packages using the following command:
sudo yum list installed
This will display a list of all packages that are currently installed on your system.